SACK-Xs Lig-8 Clonal Adult Rat Hepatocytic Stem Cells
Growing and expanding primary, differentiated adult cells in culture is difficult and laborious because many differentiated cells can only be maintained in vitro for a limited period of time. However, for controlled experiments, it may be necessary to maintain a consistent population of cells.
Maintaining a population of adult stem cells (ASCs), allows one to exponentially propagate a population of cells in vitro, and induce differentiation when desired. This is possible with SACK cell strains and specified cell culture conditions.
SACK ASC cell properties – Long-term propagation in xanthosine (Xs)-supplemented medium
- Suppressed asymmetric cell kinetics
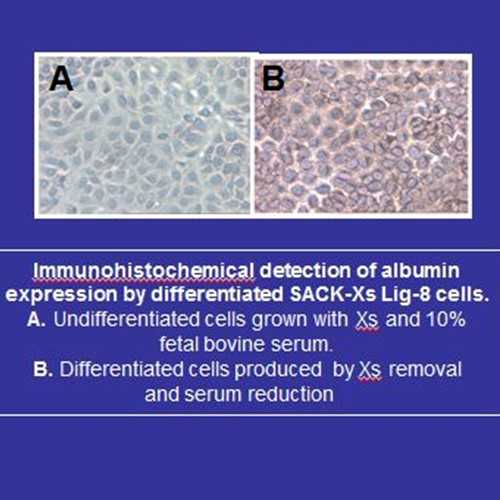
Differentiated progeny cell properties – Xs-free medium, confluent monolayer, serum reduction
Hepatocyte Properties
- Albumin secretion
- Alpha-fetoprotein secretion (indicates presence of hepatoblasts)
- Alpha 1-antitrypsin expression
- H4 hepatocyte antigen expression
- Inducible cytochrome P450 activity (CYP1A1, CYP1A2)
- Constitutive cytochrome P450 metabolism (CYP2E1)
- Spheroid formation
- Binucleation
Biliary Properties
- CK7 expression (biliary epithelial cell marker)
*Additional similar, but less well characterized, independent clonal cell strains are available. For more information, contact us.
Growing and expanding primary, differentiated adult cells in culture is difficult and laborious because many differentiated cells can only be maintained in vitro for a limited period of time. However, for controlled experiments, it may be necessary to maintain a consistent population of cells.
Maintaining a population of adult stem cells (ASCs), allows one to exponentially propagate a population of cells in vitro, and induce differentiation when desired. This is possible with SACK cell strains and specified cell culture conditions.
SACK ASC cell properties – Long-term propagation in xanthosine (Xs)-supplemented medium
- Suppressed asymmetric cell kinetics
Differentiated progeny cell properties – Xs-free medium, confluent monolayer, serum reduction
Hepatocyte Properties
- Albumin secretion
- Alpha-fetoprotein secretion (indicates presence of hepatoblasts)
- Alpha 1-antitrypsin expression
- H4 hepatocyte antigen expression
- Inducible cytochrome P450 activity (CYP1A1, CYP1A2)
- Constitutive cytochrome P450 metabolism (CYP2E1)
- Spheroid formation
- Binucleation
Biliary Properties
- CK7 expression (biliary epithelial cell marker)
*Additional similar, but less well characterized, independent clonal cell strains are available. For more information, contact us.
| Product Type: | Cell Line |
| Name: | SACK-Xs Lig-8 |
| Cell Type: | adult rat hepatocytic stem cells |
| Accession ID: | CVCL_5K99 |
| Organism: | rat |
| Source: | liver cells from adult male Fischer 344 rats |
| Morphology: | epitheliod |
| Biosafety Level: | Bsl-1 |
| Subculturing: | Passage 1:5 when cells reach approx. 80% confluence |
| Growth Conditions: | SACK medium - DMEM (4.5mg/ml high glucose) w/ 10% dialyzed FBS and 1 mM Xanthosine |
| Cryopreservation: | 70% DMEM (high glucose); 20% dialyzed FBS; 10% DMSO |
| Storage: | Liquid nitrogen |
| Shipped: | Dry ice |
Replacement of the SACK medium with differentiation conditions allows the expanded tissue stem cells to regain their in vivo homeostatic state of asymmetric self-renewal, which yields cells committed to tissue-specific differentiation.
- Sherley et al. (2010) Hepatocyte precursor cell lines. Patent No. US 7,645,610 B2.
- Taghizadeh, R. R. and Sherley, J. L. (2008) "CFP and YFP, but notGFP, provide stable fluorescent marking of rat hepatic adult stemcells,"J. Biomed. Biotech, Article ID 453590, doi:10.1155/2008/453590.
- Paré, J.-F. and Sherley, J. L. (2006) Biological principles for exvivo adult stem cell expansion, in Curr. Top. in Devel. Biol., ed. G.Schatten, Elsevier, Inc. (San Diego), Vol. 73, pp. 141-171.
- Lee, et al. (2005) EMP-1 is a junctional protein in a liver stem cellline and in the liver," Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 334, 996-1003.
- Lee et al. (2003) Clonal expansion of adult rat liver epithelial stemcells by suppression of asymmetric cell kinetics (SACK). Biotech. &Bioeng. 83, 760-771.
- Semino et al. (2003) Functional differentiation of hepatocyte-likespheroid structures from putative liver progenitor cells inthree-dimensional peptide scaffolds. Differentiation 71, 262-270.
If you publish research with this product, please let us know so we can cite your paper.