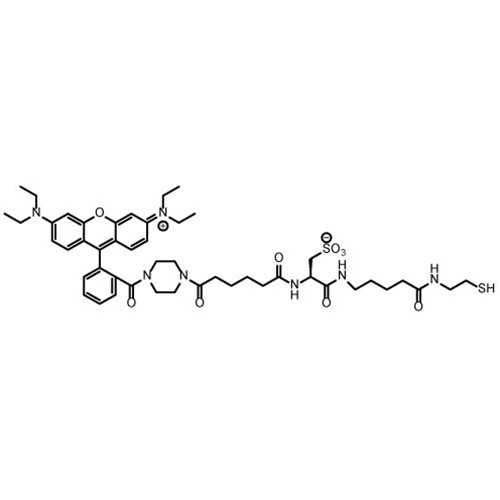
Z-Rhodamine-SH
This S-nitrosothiol reactive dye can be used to attach the rhodamine fluorophore to proteins and peptides containing S-nitrosothiol modified cysteine residues.
Highlights:
- Compatible with the Thiosulfonate Switch Technique (TST)
- Solube in water
The thiosulfonate switch technique traps protein S-nitrosothiols as mixed disulfides bearing a fluorescent probe at pH 4.0. The protocol involves initial blocking of protein thiols by S-phenylsulfonylcysteine (SPSC), which forms cysteine bearing mixed disulfides. The byproduct of the initial blocking step is benzenesulfinate itself. Subsequent addition of PhSO2Na converts protein S-nitrosothiols into protein S-phenylthiosulfonates. Addition of a highly water soluble zwitterionic rhodamine based fluorophore incorporating a reactive thiol, denoted Z-Rhodamine-SH, reacts with protein S-phenylthiosulfonates, giving rise to a mixed disulfide between the probe and the formerly S-nitrosated cysteine residue.
Also available: S-phenylsulfonylcysteine (SPSC)
From the laboratory of Paul A. Grieco, PhD, Montana State University.
 Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
This S-nitrosothiol reactive dye can be used to attach the rhodamine fluorophore to proteins and peptides containing S-nitrosothiol modified cysteine residues.
Highlights:
- Compatible with the Thiosulfonate Switch Technique (TST)
- Solube in water
The thiosulfonate switch technique traps protein S-nitrosothiols as mixed disulfides bearing a fluorescent probe at pH 4.0. The protocol involves initial blocking of protein thiols by S-phenylsulfonylcysteine (SPSC), which forms cysteine bearing mixed disulfides. The byproduct of the initial blocking step is benzenesulfinate itself. Subsequent addition of PhSO2Na converts protein S-nitrosothiols into protein S-phenylthiosulfonates. Addition of a highly water soluble zwitterionic rhodamine based fluorophore incorporating a reactive thiol, denoted Z-Rhodamine-SH, reacts with protein S-phenylthiosulfonates, giving rise to a mixed disulfide between the probe and the formerly S-nitrosated cysteine residue.
Also available: S-phenylsulfonylcysteine (SPSC)
From the laboratory of Paul A. Grieco, PhD, Montana State University.
 Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
| Product Type: | Small Molecule |
| Name: | Z-Rhodamine-SH |
| Chemical Formula: | C48H65N7O9S2 |
| Molecular Weight: | 948.21 |
| Format: | Pink powder |
| Purity: | 95+% (NMR, HPLC) |
| Solubility: | Good in water and polar organic solvents |
| Spectral Information: | Excitation maximum: 562nmExtinction at max excitation: 86,000Emission maximum: 585nmFluorescence quantum yield: 0.07 |
| Storage: | -20C. Protect from light. Dessicate |
| Shipped: | Cold packs |
- Reeves BD, Joshi N, Campanello GC, Hilmer JK, Chetia L, Vance JA, Reinschmidt JN, Miller CG, Giedroc DP, Dratz EA, Singel DJ, Grieco PA.Conversion of S-phenylsulfonylcysteine residues to mixed disulfides at pH 4.0: utility in protein thiol blocking and in protein-S-nitrosothiol detection. Org Biomol Chem. 2014 Oct 28;12(40):7942-56.
If you publish research with this product, please let us know so we can cite your paper.