Human Fibronectin III 1,2 N-GST
This recombinant FN fragment corresponds to amino acids S578-T778 of type type-III 1-2.
Fibronectins (FN) are a family of high molecular weight, multidomain glycoproteins composed of two structurally similar subunits which are joined at the carboxyl terminus by disulfide bonds. The primary structure of FN is organized into three types of repeating homologous units, termed types I, II, and III. These modules in turn are organized into functional domains which have been shown to contain multiple binding sites, including those for sulfated glycosaminoglycans, gelatin, fibrin, and cell surface integrin receptors. Twelve type I modules are found grouped at the amino- and carboxyl-terminal regions, and two type II modules are located within the gelatin-binding region. Fifteen to seventeen type III modules are contained within the middle of the molecule and comprise 60% of fibronectin’s sequence.
From the laboratory of Denise C. Hocking, PhD, University of Rochester Medical Center.
 Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
This recombinant FN fragment corresponds to amino acids S578-T778 of type type-III 1-2.
Fibronectins (FN) are a family of high molecular weight, multidomain glycoproteins composed of two structurally similar subunits which are joined at the carboxyl terminus by disulfide bonds. The primary structure of FN is organized into three types of repeating homologous units, termed types I, II, and III. These modules in turn are organized into functional domains which have been shown to contain multiple binding sites, including those for sulfated glycosaminoglycans, gelatin, fibrin, and cell surface integrin receptors. Twelve type I modules are found grouped at the amino- and carboxyl-terminal regions, and two type II modules are located within the gelatin-binding region. Fifteen to seventeen type III modules are contained within the middle of the molecule and comprise 60% of fibronectin’s sequence.
From the laboratory of Denise C. Hocking, PhD, University of Rochester Medical Center.
 Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
| Product Type: | Protein |
| Name: | Recombinant Human Fibronectin III 1,2; amino acids S578-T778 |
| Accession ID: | Q9H6D8, Q5VTL7, Q8TC99, Q8BJN4 |
| Source: | Human protein expressed in E. coli DH5 alpha carrying the cloned gene in pGEX-2T |
| Molecular Weight: | 48548.1 Da |
| Amino Acid Sequence: | SGPVEVFITETPSQPNSHPIQWNAPQPSHISKYILRWRPKNSVGRWKEATIPGHLNSYTIAGLKPGVVYEGQLISIQQYGHQEVTRFDFTTTSTSTPVTSNTVTGETTPFSPLVATSESVTEITASSFVVSWVSASDTVSGFRVEYELSEEGDEPQYLALPSTATSVNIPDLLPGRKYIVNVYQISEDGEQSLILSTSQTT |
| Fusion Tag(s): | GST, N-terminal |
| Purity: | > 90% by SDS-PAGE |
| Buffer: | Solution in PBS |
| Concentration: | 0.7mg/mL |
| Storage: | Store at -80C |
| Shipped: | Dry ice |
. |
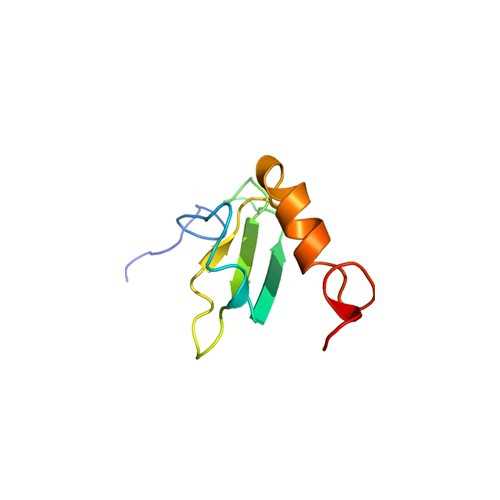
| FNIII 1-2 Solution Structure. Secondary structure elements are colored cyan and purple for FNIII 1 and FNIII 2, respectively. Adapted from: Vakonakis, I., Staunton, D., Rooney, L.M., and Campbell, I. D. (2007) Interdomain association in fibronectin: insight into cryptic sites and fibrillogenesis. EMBO J. 26: 2575-2583. |
 |
| Schematic representation of a fibronectin subunit and recombinant fibronectin fusion protein. |
- Hocking, D.C., Smith, R.K., and McKeown-Longo, P.J. (1996) A novel role for the integrin-binding III10 module in fibronectin matrix assembly. J. Cell Biol. 133:431-444.
If you publish research with this product, please let us know so we can cite your paper.