Anti-MUC1 [CD-1] Antibody
This IgG1 kappa antibody was generated against recombinant human MUC1-C cytoplasmic domain (MUC1-CD) and recognizes an epitope (NYGQLDIFP) between amino acids 7 and 15.
Anti-MUC1 (CD-1) is ideal for Western Blot (WB) and Immunoprecipitation (IP) experiments.
Mucin 1 (MUC1) is aberrantly overexpressed in diverse human carcinomas and certain hematologic malignancies, and is an attractive target for drug development. MUC1 consists of two subunits; the MUC1 C-terminal (MUC1-C) subunit is an oncoprotein and cancer target. The MUC1-C subunit contains an extracellular domain, a transmembrane region, and a cytoplasmic domain. The MUC1-C cytoplasmic domain (CD) has been shown to interact with effectors such as PI3K, NF-kappaB, and Beta-Catenin which have all been linked to transformation. The MUC1-C cytoplasmic domain also contains a CQC motif necessary for dimerization, interaction with effectors, and nuclear localization. Cell-penetrating peptides and small molecules have been designed to block this site, one of which is currently in Phase I clinical evaluation. As vaccines and drugs are well under development against MUC1, antibodies will serve as useful biomarkers to define those patients who express MUC1-C and are thus likely to respond.
From the laboratory of Donald W. Kufe, MD, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute.
 Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
This IgG1 kappa antibody was generated against recombinant human MUC1-C cytoplasmic domain (MUC1-CD) and recognizes an epitope (NYGQLDIFP) between amino acids 7 and 15.
Anti-MUC1 (CD-1) is ideal for Western Blot (WB) and Immunoprecipitation (IP) experiments.
Mucin 1 (MUC1) is aberrantly overexpressed in diverse human carcinomas and certain hematologic malignancies, and is an attractive target for drug development. MUC1 consists of two subunits; the MUC1 C-terminal (MUC1-C) subunit is an oncoprotein and cancer target. The MUC1-C subunit contains an extracellular domain, a transmembrane region, and a cytoplasmic domain. The MUC1-C cytoplasmic domain (CD) has been shown to interact with effectors such as PI3K, NF-kappaB, and Beta-Catenin which have all been linked to transformation. The MUC1-C cytoplasmic domain also contains a CQC motif necessary for dimerization, interaction with effectors, and nuclear localization. Cell-penetrating peptides and small molecules have been designed to block this site, one of which is currently in Phase I clinical evaluation. As vaccines and drugs are well under development against MUC1, antibodies will serve as useful biomarkers to define those patients who express MUC1-C and are thus likely to respond.
From the laboratory of Donald W. Kufe, MD, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute.
 Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
| Product Type: | Antibody |
| Antigen: | Muc1-Cytoplasmic Domain (MUC1-CD) |
| Accession ID: | P15941 |
| Isotype: | IgG1 kappa |
| Clonality: | Monoclonal |
| Clone Name: | CD-1 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Immunogen: | Purified protein |
| Species Immunized: | Mouse |
| Epitope: | NYGQLDIFP |
| Purification Method: | Affinity chromatograpy |
| Method Used to Determine Concentration: | Nanodrop |
| Buffer: | PBS, 0.05% (w/v) Sodium Azide |
| Tested Applications: | WB, IP |
| Concentration: | 1mg/mL |
| Storage: | 4C (working) -20C or -80C (stock) |
| Shipped: | Cold packs |
Immunoblot and immunoprecipitation analyses with anti-MUC1-CD.
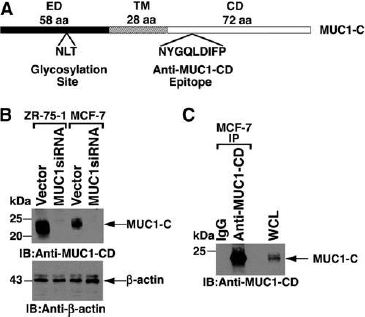
(A) Schematic of oncogenic MUC1-Csubunit with the 58 aa extracellular domain (ED), the 28 aatransmembrane region (TM), and the 72 aa cytoplasmic domain(CD). Highlighted are the sites for N-glycosylation inthe ED and for anti-MUC1-CD binding in the CD. (B) Lysatesfrom the indicated cell lines were immunoblotted withanti-MUC1-CD and anti-b-actin. (C) Lysates from MCF-7cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-MUC1-CD or, as acontrol, IgG. The precipitates were immunoblotted with anti-MUC1-CD.
Adapted from: Panchamoorthy G, Rehan H, Kharbanda A, Ahmad R, Kufe, D. A monoclonal antiboyd against the oncogenic mucin 1 cytoplasmic domain. Hybridoma, 30(6):531-535 (2011).
The extracellular domain is subject to glycosylation at the third asparagine residue. As such, MUC1-C in cell lysates is detectable as a broad 20-25 kDa glycosylated form.
- Panchamoorthy G, Rehan H, Kharbanda A, Ahmad R, Kufe, D. A monoclonal antiboyd against the oncogenic Mucin 1 cytoplasmic domain. Hybridoma, 30(6):531-535 (2011).
- Kufe, DW. MUC1-C oncoprotein as a target in breast cancer: activation of signaling pathways and therapeutic approaches. Oncogene, 1-9 (2012).
- Kufe, DW. Mucins in cancer: function,prognosis and therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 9(12):874-85 (2009).
If you publish research with this product, please let us know so we can cite your paper.

![Anti-MUC1 [CD-1] Antibody Anti-MUC1 [CD-1] Antibody](https://www.kerafast.com/MediaStorage/Product/Images/Medium/731_200120200126197300.jpg)
