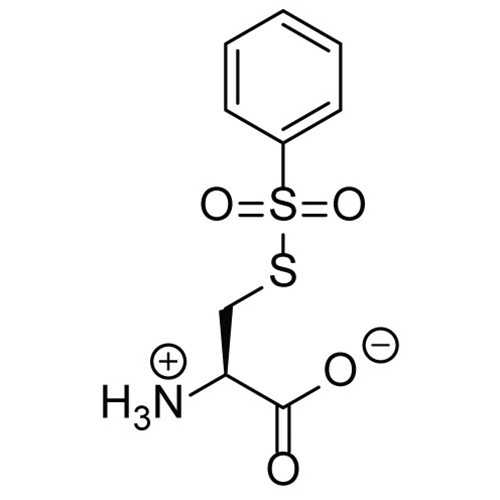
S-phenylsulfonylcysteine (SPSC)
This reagent can be used to block thiols (SH) in proteins and peptides containing cysteine residues, as well as other thiolated molecules (such as thiol-containing oligonucleotides) at room temperature. Free thiols are converted to SSCys residues and an equivalent of PhSO- are produced.
Highlights:
- Most efficient at lower pH
- SPSC is utilized in the Thiosulfonate Switch Technique (TST)
- Solube in water
The thiosulfonate switch technique traps protein S-nitrosothiols as mixed disulfides bearing a fluorescent probe at pH 4.0. The protocol involves initial blocking of protein thiols by S-phenylsulfonylcysteine (SPSC), which forms cysteine bearing mixed disulfides. The byproduct of the initial blocking step is benzenesulfinate itself. Subsequent addition of PhSO2Na converts protein S-nitrosothiols into protein S-phenylthiosulfonates. Addition of a highly water soluble zwitterionic rhodamine based fluorophore incorporating a reactive thiol, denoted Z-Rhodamine-SH, reacts with protein S-phenylthiosulfonates, giving rise to a mixed disulfide between the probe and the formerly S-nitrosated cysteine residue.
Also available: Z-Rhodamine-SH
From the laboratory of Paul A. Grieco, PhD, Montana State University.
 Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
This reagent can be used to block thiols (SH) in proteins and peptides containing cysteine residues, as well as other thiolated molecules (such as thiol-containing oligonucleotides) at room temperature. Free thiols are converted to SSCys residues and an equivalent of PhSO
Highlights:
- Most efficient at lower pH
- SPSC is utilized in the Thiosulfonate Switch Technique (TST)
- Solube in water
The thiosulfonate switch technique traps protein S-nitrosothiols as mixed disulfides bearing a fluorescent probe at pH 4.0. The protocol involves initial blocking of protein thiols by S-phenylsulfonylcysteine (SPSC), which forms cysteine bearing mixed disulfides. The byproduct of the initial blocking step is benzenesulfinate itself. Subsequent addition of PhSO2Na converts protein S-nitrosothiols into protein S-phenylthiosulfonates. Addition of a highly water soluble zwitterionic rhodamine based fluorophore incorporating a reactive thiol, denoted Z-Rhodamine-SH, reacts with protein S-phenylthiosulfonates, giving rise to a mixed disulfide between the probe and the formerly S-nitrosated cysteine residue.
Also available: Z-Rhodamine-SH
From the laboratory of Paul A. Grieco, PhD, Montana State University.
 Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
| Product Type: | Small Molecule |
| Name: | S-phenylsulfonylcysteine (SPSC) |
| Chemical Formula: | C9H11NO4S2 |
| Molecular Weight: | 261.31 |
| Format: | White powder |
| Purity: | 95+% (NMR) |
| Solubility: | Good in water and polar organic solvents |
| Comments: | Do not store this reagent in water |
| Storage: | -20C. Protect from light. Dessicate |
| Shipped: | Cold packs |
Conversion of SPSC

% Conversion of SPSC to PhSO2Na over 1h as measured from absorbance detection at 265 nm from RP HPLC analysis.
Adapted from: Reeves BD, et al. Org Biomol Chem. 2014 Oct 28;12(40):7942-56.
- Reeves BD, Joshi N, Campanello GC, Hilmer JK, Chetia L, Vance JA, Reinschmidt JN, Miller CG, Giedroc DP, Dratz EA, Singel DJ, Grieco PA.Conversion of S-phenylsulfonylcysteine residues to mixed disulfides at pH 4.0: utility in protein thiol blocking and in protein-S-nitrosothiol detection. Org Biomol Chem. 2014 Oct 28;12(40):7942-56.
If you publish research with this product, please let us know so we can cite your paper.