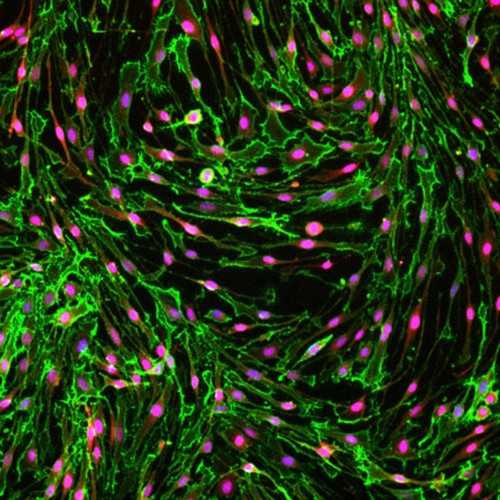
Rat Primary Schwann Cells
Primary Schwann cells isolated from adult rat sciatic nerve and purified via magnetic activated cell sorting.
Highlights
- Highly pure (>98%) Schwann cells - Identified on the basis of double immunostaining with the Schwann cell-specific markers, S100 and p75NGFR
- Exhibit typical elongated (bipolar) phenotype and capacity to express myelin-associated genes upon stimulation with differentiating factors
- Adhere to substrate and extend processes within 1-2 hours after plating and continue to actively proliferate in the presence of mitogenic factors
- Expandable through successive rounds of subculture in vitro for at least 3-4 additional passages without losing phenotypic characteristics or biological activity
The culture of primary Schwann cells provides a unique in vitro system for basic research, preclinical drug discovery, neurotoxicity testing, and in vitro modeling of aging, cancer and disease conditions affecting the myelin sheaths. Schwann cell transplantation in experimental animals remains a promising strategy to investigate mechanisms of repair and myelination in the central and peripheral nervous system.
From the laboratory of Paula V. Monje, PhD, University of Miami.
Primary Schwann cells isolated from adult rat sciatic nerve and purified via magnetic activated cell sorting.
Highlights
- Highly pure (>98%) Schwann cells - Identified on the basis of double immunostaining with the Schwann cell-specific markers, S100 and p75NGFR
- Exhibit typical elongated (bipolar) phenotype and capacity to express myelin-associated genes upon stimulation with differentiating factors
- Adhere to substrate and extend processes within 1-2 hours after plating and continue to actively proliferate in the presence of mitogenic factors
- Expandable through successive rounds of subculture in vitro for at least 3-4 additional passages without losing phenotypic characteristics or biological activity
The culture of primary Schwann cells provides a unique in vitro system for basic research, preclinical drug discovery, neurotoxicity testing, and in vitro modeling of aging, cancer and disease conditions affecting the myelin sheaths. Schwann cell transplantation in experimental animals remains a promising strategy to investigate mechanisms of repair and myelination in the central and peripheral nervous system.
From the laboratory of Paula V. Monje, PhD, University of Miami.
| Product Type: | Cell Line |
| Name: | Rat Primary Schwann Cells |
| Cell Type: | Primary adult peripheral nerve Schwann cells |
| Morphology: | Elongated, spindle-shaped |
| Source: | Sciatic nerve |
| Organism: | Rat (Sprague Dawley) |
| Biosafety Level: | BSL-1 |
| Growth Conditions: | DMEM / 10% FBS, 10 nM neuregulin, 2 µM forskolin |
| Cryopreservation: | 10% DMSO / 90% FBS |
| Amount: | 106 cells/mL |
| Storage: | Liquid nitrogen |
| Shipped: | Dry Ice |
Schwann cells are obtained from the sciatic nerve of adult 3 month old rats using a novel protocol for immediate dissociation and purification by magnetic activated cell sorting (MACS). Schwann cells maintain their identity, viability and growth rates throughout the process of isolation, purification, expansion and cryopreservation. The cryopreserved product consists of MACS-purified rat Schwann cells identified as S100 positive, p75NGFR positive, GFAP positive cells. The absence of fibroblast contamination is determined on the basis of the lack of expression of Thy-1, a fibroblast-specific marker. These cells actively proliferate in response to defined mitogenic factors and increase the expression of myelination-associated genes in response to cAMP treatment, which are key indicators of preservation of biological activity.
Schwann cell cultures established from cryopreserved stocks are viable (>90% at 24 hs post-plating), expandable and homogeneous. Cells exhibit typical features of cultured Schwann cells including as ability to align to one another forming typical bundles of cells. Cells can be subcultured in media containing neuregulin and forskolin as mitogenic factors. NOTE: Excessive passaging is not recommended due to possible phenotypic derivation of the cells typically without transformation. Cells can be cryopreserved at essentially any passage.
- Andersen ND, Srinivas S, Piñero G, Monje PV. A rapid and versatile method for the isolation, purification and cryogenic storage of Schwann cells from adult rodent nerves. Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 23;6:31781. doi: 10.1038/srep31781. View Article
- Andersen ND, Monje PV. Isolation, Culture, and Cryopreservation of Adult Rodent Schwann Cells Derived from Immediately Dissociated Teased Fibers. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1739:49-66. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7649-2_4. PubMed PMID: 29546700.
- Ravelo KM, Andersen ND, Monje PV. Magnetic-Activated Cell Sorting for the Fast and Efficient Separation of Human and Rodent Schwann Cells from Mixed Cell Populations. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1739:87-109. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7649-2_6. PubMed PMID: 29546702.
- Li R, Li D, Wu C, et al. Nerve growth factor activates autophagy in Schwann cells to enhance myelin debris clearance and to expedite nerve regeneration. Theranostics. 2020;10(4):1649-1677. Published 2020 Jan 1.View article
- Fogarty EA, Kitzman JO, Antonellis A. SOX10-regulated promoter use defines isoform-specific gene expression in Schwann cells. BMC Genomics. 2020;21(1):549. Published 2020 Aug 8. View article
If you publish research with this product, please let us know so we can cite your paper.